What is Sensorial in Montessori? First we need to understand the meaning of sensorial. The word Sensorial means sense or feeling. Children cannot learn anything new from their work. Children often focus on all their senses, from the visual to the stereognosis.
Are you exciting for having knowledge about sensorial Montessori. This is very important for your child’s progress. In this post we will explore the areas of sensorial in Montessori. Keep reading.

What is the purpose of a sensorial in Montessori?
An area in the Montessori classroom called the Sensory Zone which is used to focus children on different lessons, also known as the Applebee. Sensory classrooms help children understand the five senses. Like tasting, touching, seeing, and hearing.
The main purpose of creating classrooms is to teach children how the world around them is, what is going on in the world around them, and how to see things. These classrooms have all the materials to help how a child correct basic mistakes. Thanks to the system, the child gets into the habit of paying attention to his mistakes and the children learn a lot from the mistakes. When children move around freely If they move around, they develop the ability to do all the work by themselves.
The Designed Material For Sensorial
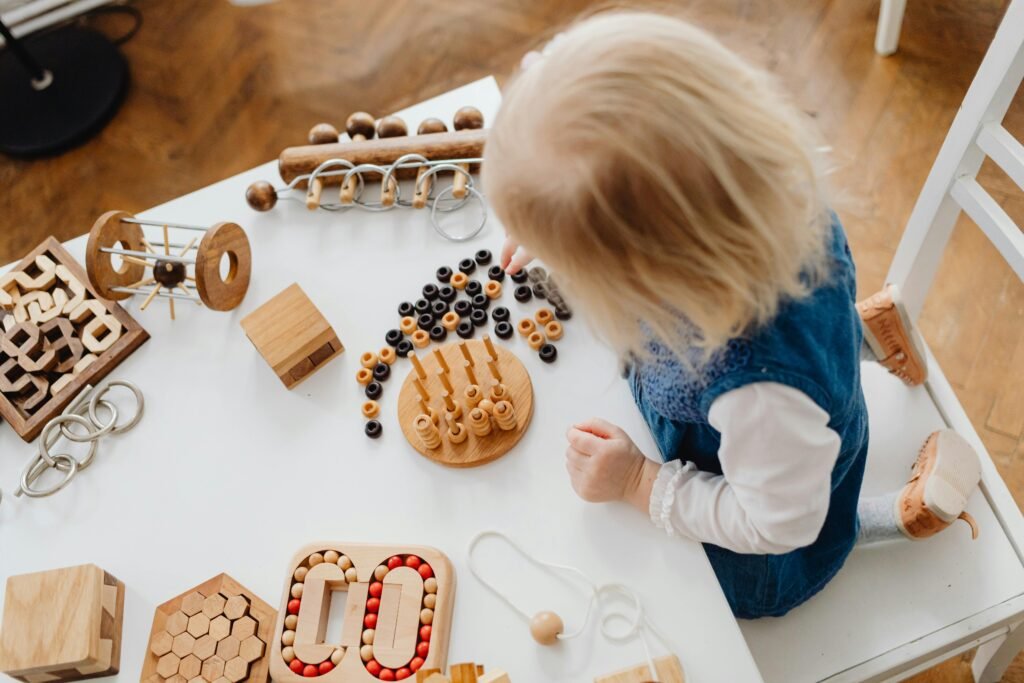

What is Sensorial in Montessori? The material collected for organizing the sensory work came with the help of two doctors viz Attard and Seguin. They have gathered their ideas and observations to create this material that can develop sensory ability in children. This material defines practical life. What is it, he is completely ignorant about? He doesn’t know anything about the benefits of using this material and how it can be used. They need to be improved so that the content is presented to children in a way that allows them to have a new experience. And use things they don’t know about so they can think in new ways and express their ideas. The same considerations have been kept in mind while designing the content.

- Sensory content allows the child to focus his attention to work
- Error control provides the child with a position to self-correct the error
- All of these materials are similar to everyday life, allowing the child to disassemble and reassemble to create and try new things.
- Whatever provided material on which the child is working is missing, the child can complete his work without a missing piece, i.e. even if a piece is lost, the child can continue his game without it.
- Children are provided with limited materials. Sometimes a piece that one child has, it is given to another child and when he has completed his work, he returns the piece to the first child. It develops patience in the child and he gets to know the colors of the world and tries to cooperate with others.
- A child learns by doing different kinds of experiences to develop his abilities keeping in view his interest
- These objects are “material abstraction”.
Sensorial work comprises 8 groups-Visual, Tactile, Baric, Thermic, Auditory, Olfactory and Gustatory & Stereognosis

Visual
Visual Group With the help of the child, the child learns to feel the difference between different objects such as which object is small and which is big or which object is matching with which. Stairs and red rods help children visually understand and learn about a variety of experiences .
Tactile
Children don’t know much about their own touch. This material includes resources to help children understand what touch is. Children use body parts such as fingers to handle materials. Children will learn to count on their fingers and learn to feel things by touching them with their fingers, so they will feel their touch. In these groups, mystery bags and touch boards are placed so that with the help of these objects, children can understand the senses.
Baric
Kids can’t tell the difference between weight and pressure. Baric includes a variety of objects to help kids learn the difference between weight and pressure.
Thermal
Thermic bottles and thermic pills are present in classes of children so that thermal materials could improve the baby’s temperature.
Auditory
Young children don’t understand the difference between sounds. These lessons use Auditory boxes to help children understand the difference between sounds and help them feel the difference between different sounds.
Olfactory and Gustatory
To describe children’s the sense of smell and taste, Olfactory and Gustatory lessons researched it. In order to give the knowledge about how to taste things and feel the sense of smell to children.
Stereognostic
This sensory content includes lessons to develop children’s sensory abilities so that children can recognize the sense of sight, smell, taste, hearing, touch. Young children do not know anything about their senses when Until we give information. Our surroundings provide with a lot of information about sensory lessons such as what kinds of shapes children see, what things they feel, what children play outside. When they play outside the house they see things what they look like, are they small or big, do they know about smooth and rough objects, do they smell anything, what smells good and what smells bad, even at home. So they learn a lot from an environment and improve their senses.
What is Sensorial in Montessori? We must know about sensorial to know all the aspects for the growth of our child. They recognize their movements and thinking, then it will help them to become a conscious person of the society. It introduces a method of fully realizing their potential. This post will help you to understand all sensorial materials.
Interested Post:
- Liberty University Library Resources: Comprehensive Guide.
- Empowering Panorama Education: Unlocking Student Potential.
- https://waostudy.com/importance-of-educational-finance-finance-education-principles-and-types/
- https://waostudy.com/why-is-montessori-education-important-for-children-montessori-is-a-playful-learning/
- https://waostudy.com/9-montessori-education-principles-montessori-curriculum-model/